# 项目搭建规范
# 一。代码规范
# 1.1. 集成 editorconfig 配置
EditorConfig 有助于为不同 IDE 编辑器上处理同一项目的多个开发人员维护一致的编码风格。
# http://editorconfig.org | |
root = true | |
[*] # 表示所有文件适用 | |
charset = utf-8 # 设置文件字符集为 utf-8 | |
indent_style = space # 缩进风格(tab | space) | |
indent_size = 2 # 缩进大小 | |
end_of_line = lf # 控制换行类型 (lf | cr | crlf) | |
trim_trailing_whitespace = true # 去除行首的任意空白字符 | |
insert_final_newline = true # 始终在文件末尾插入一个新行 | |
[*.md] # 表示仅 md 文件适用以下规则 | |
max_line_length = off | |
trim_trailing_whitespace = false |
VSCode 需要安装一个插件:EditorConfig for VS Code
# 1.2. 使用 prettier 工具
Prettier 是一款强大的代码格式化工具,支持 JavaScript、TypeScript、CSS、SCSS、Less、JSX、Angular、Vue、GraphQL、JSON、Markdown 等语言,基本上前端能用到的文件格式它都可以搞定,是当下最流行的代码格式化工具。
1. 安装 prettier
npm install prettier -D |
2. 配置.prettierrc 文件:
- useTabs:使用 tab 缩进还是空格缩进,选择 false;
- tabWidth:tab 是空格的情况下,是几个空格,选择 2 个;
- printWidth:当行字符的长度,推荐 80,也有人喜欢 100 或者 120;
- singleQuote:使用单引号还是双引号,选择 true,使用单引号;
- trailingComma:在多行输入的尾逗号是否添加,设置为
none; - semi:语句末尾是否要加分号,默认值 true,选择 false 表示不加;
{ | |
"useTabs": false, | |
"tabWidth": 2, | |
"printWidth": 80, | |
"singleQuote": true, | |
"trailingComma": "none", | |
"semi": false | |
} |
3. 创建.prettierignore 忽略文件
/dist/*
.local
.output.js
/node_modules/**
**/*.svg
**/*.sh
/public/*
4.VSCode 需要安装 prettier 的插件
5. 测试 prettier 是否生效
- 测试一:在代码中保存代码;
- 测试二:配置一次性修改的命令;
在 package.json 中配置一个 scripts:
"prettier": "prettier --write ." |
# 1.3. 使用 ESLint 检测
1. 在前面创建项目的时候,我们就选择了 ESLint,所以 Vue 会默认帮助我们配置需要的 ESLint 环境。
2.VSCode 需要安装 ESLint 插件:

3. 解决 eslint 和 prettier 冲突的问题:
安装插件:(vue 在创建项目时,如果选择 prettier,那么这两个插件会自动安装)
npm i eslint-plugin-prettier eslint-config-prettier -D |
添加 prettier 插件:(在.eslintrc.js 文件中)
module.exports = { | |
root: true, | |
env: { | |
node: true | |
}, | |
extends: [ | |
'plugin:vue/vue3-essential', | |
'eslint:recommended', | |
'@vue/typescript/recommended', | |
'plugin:prettier/recommended' // 加上这句话,一般会自动加 | |
], | |
parserOptions: { | |
ecmaVersion: 2020 | |
}, | |
rules: { | |
'no-console': process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? 'warn' : 'off', | |
'no-debugger': process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? 'warn' : 'off' | |
} | |
} |
# 1.4. git Husky 和 eslint
虽然我们已经要求项目使用 eslint 了,但是不能保证组员提交代码之前都将 eslint 中的问题解决掉了:
也就是我们希望保证代码仓库中的代码都是符合 eslint 规范的;
那么我们需要在组员执行
git commit命令的时候对其进行校验,如果不符合 eslint 规范,那么自动通过规范进行修复;
那么如何做到这一点呢?可以通过 Husky 工具:
- husky 是一个 git hook 工具,可以帮助我们触发 git 提交的各个阶段:pre-commit、commit-msg、pre-push
如何使用 husky 呢?
这里我们可以使用自动配置命令:
npx husky-init npm install |
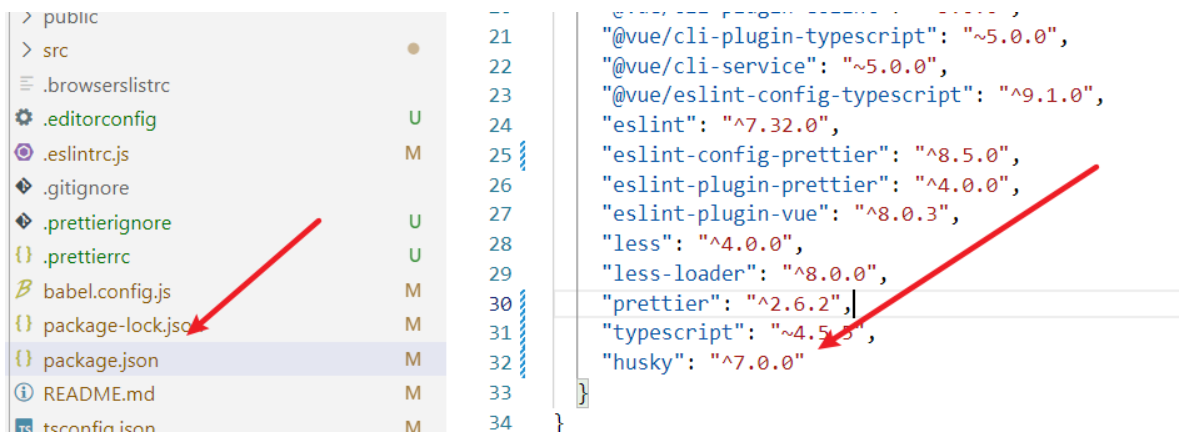
这里会做三件事:
1. 安装 husky 相关的依赖:
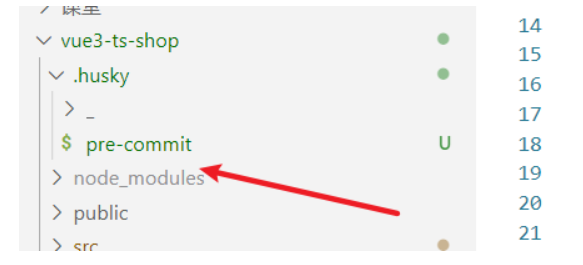
2. 在项目目录下创建 .husky 文件夹:
npx huksy install
3. 在 package.json 中添加一个脚本:

接下来,我们需要去完成一个操作:在进行 commit 时,执行 lint 脚本:
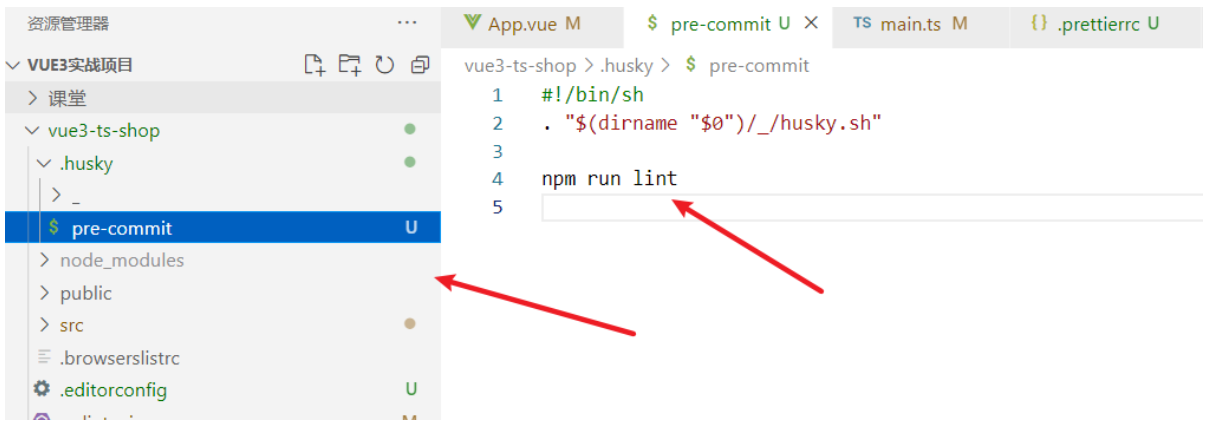
这个时候我们执行 git commit 的时候会自动对代码进行 lint 校验。
# 1.5. git commit 规范
# 1.5.1. 代码提交风格
通常我们的 git commit 会按照统一的风格来提交,这样可以快速定位每次提交的内容,方便之后对版本进行控制。
但是如果每次手动来编写这些是比较麻烦的事情,我们可以使用一个工具:Commitizen
- Commitizen 是一个帮助我们编写规范 commit message 的工具;
1. 安装 Commitizen
npm install commitizen -D |
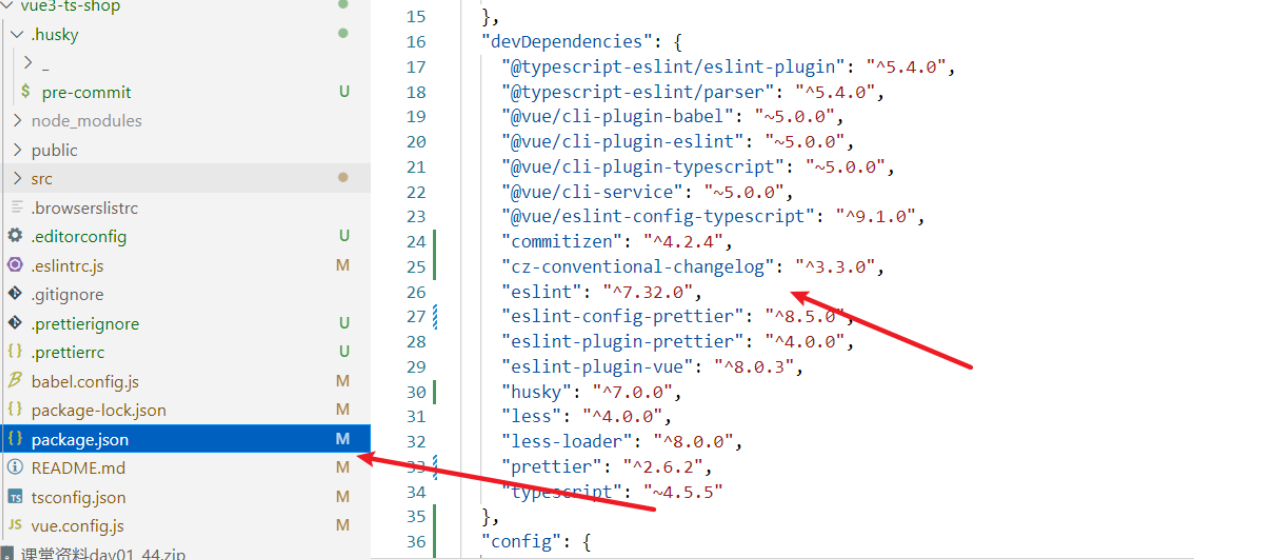
2. 安装 cz-conventional-changelog,并且初始化 cz-conventional-changelog:
npx commitizen init cz-conventional-changelog --save-dev --save-exact |
这个命令会帮助我们安装 cz-conventional-changelog:
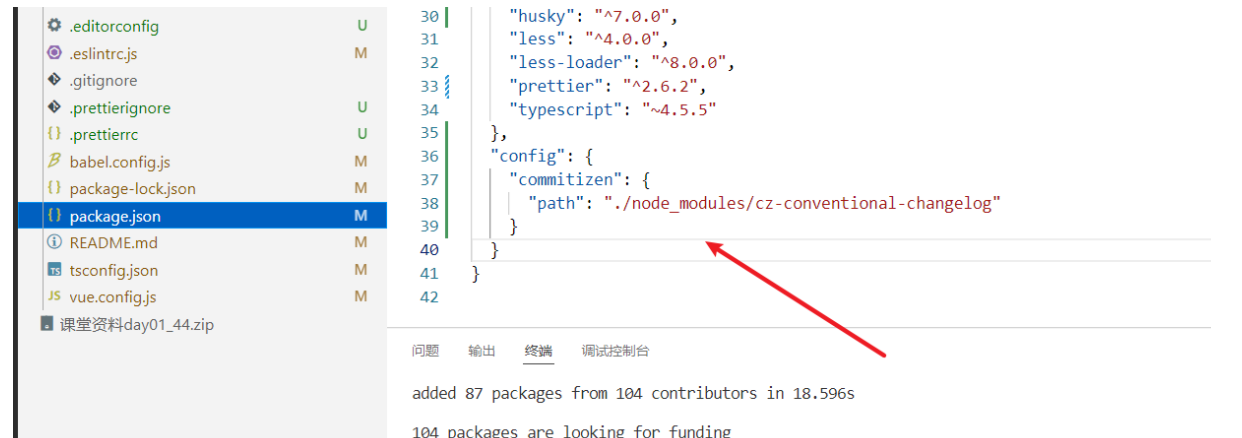
并且在 package.json 中进行配置:
这个时候我们提交代码需要使用 npx cz :
- 第一步是选择 type,本次更新的类型
| Type | 作用 |
|---|---|
| feat | 新增特性 (feature) |
| fix | 修复 Bug (bug fix) |
| docs | 修改文档 (documentation) |
| style | 代码格式修改 (white-space, formatting, missing semi colons, etc) |
| refactor | 代码重构 (refactor) |
| perf | 改善性能 (A code change that improves performance) |
| test | 测试 (when adding missing tests) |
| build | 变更项目构建或外部依赖(例如 scopes: webpack、gulp、npm 等) |
| ci | 更改持续集成软件的配置文件和 package 中的 scripts 命令,例如 scopes: Travis, Circle 等 |
| chore | 变更构建流程或辅助工具 (比如更改测试环境) |
| revert | 代码回退 |
- 第二步选择本次修改的范围(作用域)

- 第三步选择提交的信息

- 第四步提交详细的描述信息

- 第五步是否是一次重大的更改

- 第六步是否影响某个 open issue

我们也可以在 scripts 中构建一个命令来执行 cz:
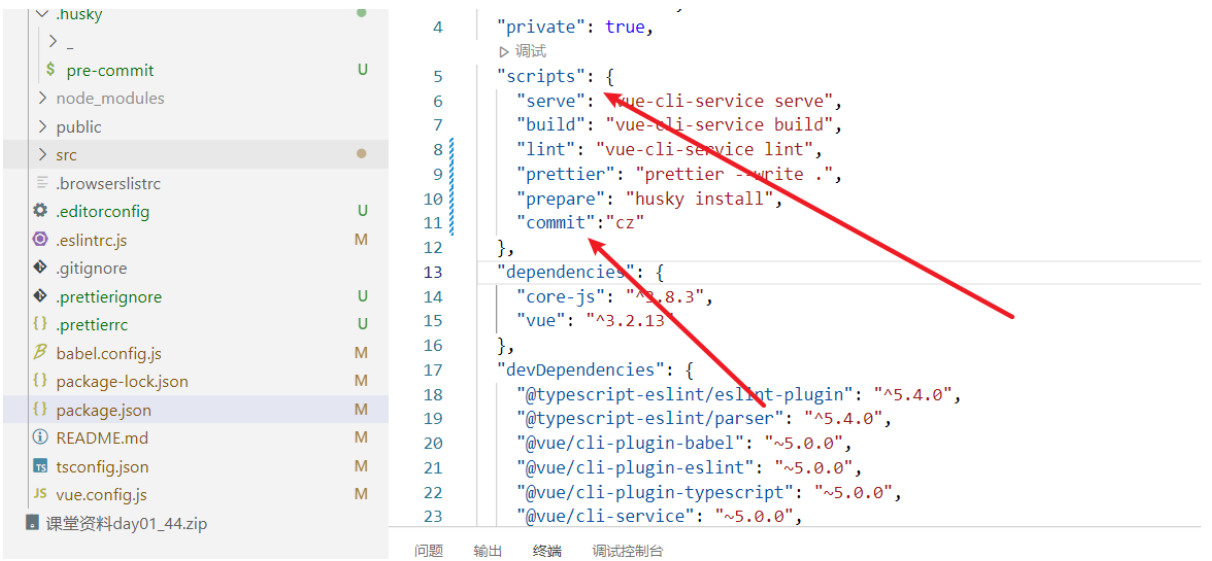
# 1.5.2. 代码提交验证
如果我们按照 cz 来规范了提交风格,但是依然有同事通过 git commit 按照不规范的格式提交应该怎么办呢?
- 我们可以通过 commitlint 来限制提交;
1. 安装 @commitlint/config-conventional 和 @commitlint/cli
npm i @commitlint/config-conventional @commitlint/cli -D |
2. 在根目录创建 commitlint.config.js 文件,配置 commitlint
module.exports = { | |
extends: ['@commitlint/config-conventional'] | |
} |
3. 使用 husky 生成 commit-msg 文件,验证提交信息:
npx husky add .husky/commit-msg "npx --no-install commitlint --edit $1" |
# 二。第三方库集成
# 2.1. vue.config.js 配置
vue.config.js 有三种配置方式:
- 方式一:直接通过 CLI 提供给我们的选项来配置:
- 比如 publicPath:配置应用程序部署的子目录(默认是
/,相当于部署在https://www.my-app.com/); - 比如 outputDir:修改输出的文件夹;
- 比如 publicPath:配置应用程序部署的子目录(默认是
- 方式二:通过 configureWebpack 修改 webpack 的配置:
- 可以是一个对象,直接会被合并;
- 可以是一个函数,会接收一个 config,可以通过 config 来修改配置;
- 方式三:通过 chainWebpack 修改 webpack 的配置:
- 是一个函数,会接收一个基于 webpack-chain 的 config 对象,可以对配置进行修改;
const path = require('path') | |
module.exports = { | |
outputDir: './build', | |
// configureWebpack: { | |
// resolve: { | |
// alias: { | |
// views: '@/views' | |
// } | |
// } | |
// } | |
// configureWebpack: (config) => { | |
// config.resolve.alias = { | |
// '@': path.resolve(__dirname, 'src'), | |
// views: '@/views' | |
// } | |
// }, | |
chainWebpack: (config) => { | |
config.resolve.alias.set('@', path.resolve(__dirname, 'src')).set('views', '@/views') | |
} | |
} |
# 2.2. vue-router 集成
安装 vue-router 的最新版本:
npm install vue-router@next |
创建 router 对象:(在 src 目录下创建 router 文件夹 /index.ts)
import { createRouter, createWebHashHistory } from 'vue-router' | |
import type { RouteRecordRaw } from 'vue-router' | |
const routes: RouteRecordRaw[] = [ | |
{ | |
path: '/', | |
redirect: '/main' | |
}, | |
{ | |
path: '/main', | |
component: () => import('../views/main/main.vue') | |
}, | |
{ | |
path: '/login', | |
component: () => import('../views/login/login.vue') | |
} | |
] | |
const router = createRouter({ | |
routes, | |
history: createWebHashHistory() | |
}) | |
export default router |
安装 router:
import router from './router' | |
createApp(App).use(router).mount('#app') |
在 App.vue 中配置跳转:
<template> | |
<div id="app"> | |
<router-link to="/login">登录</router-link> | |
<router-link to="/main">首页</router-link> | |
<router-view></router-view> | |
</div> | |
</template> |
# 2.3. vuex 集成
安装 vuex:
npm install vuex@next |
创建 store 对象:(在 src 目录下创建 store 文件夹 /index.ts)
import { createStore } from 'vuex' | |
const store = createStore({ | |
state() { | |
return { | |
name: 'coderwhy' | |
} | |
} | |
}) | |
export default store |
安装 store:
createApp(App).use(router).use(store).mount('#app') |
在 App.vue 中使用:
<h2></h2> |
# 2.4. element-plus 集成
Element Plus,一套为开发者、设计师和产品经理准备的基于 Vue 3.0 的桌面端组件库:
- 相信很多同学在 Vue2 中都使用过 element-ui,而 element-plus 正是 element-ui 针对于 vue3 开发的一个 UI 组件库;
- 它的使用方式和很多其他的组件库是一样的,所以学会 element-plus,其他类似于 ant-design-vue、NaiveUI、VantUI 都是差不多的;
安装 element-plus
npm install element-plus |
# 2.4.1. 全局引入
一种引入 element-plus 的方式是全局引入,代表的含义是所有的组件和插件都会被自动注册:
// main.ts | |
import { createApp } from 'vue' | |
import ElementPlus from 'element-plus' | |
import 'element-plus/dist/index.css' | |
import App from './App.vue' | |
const app = createApp(App) | |
app.use(ElementPlus) | |
app.mount('#app') |
引入字体图标
// main.ts | |
// 引入 element plus 图标 | |
import * as ElIcons from '@element-plus/icons-vue' | |
// 统一注册 Icon 图标 | |
for (const iconName in ElIcons) { | |
app.component(iconName, ElIcons[iconName]) | |
} |
# 2.4.2. 按需引入
首先你需要安装 unplugin-vue-components 和 unplugin-auto-import 这两款插件
npm install -D unplugin-vue-components unplugin-auto-import |
在 vue.config.js 中配置
const { defineConfig } = require('@vue/cli-service')
const AutoImport = require('unplugin-auto-import/webpack')
const Components = require('unplugin-vue-components/webpack')
const { ElementPlusResolver } = require('unplugin-vue-components/resolvers')
module.exports = defineConfig({
configureWebpack: {
// ...
plugins: [
AutoImport({
resolvers: [ElementPlusResolver()]
}),
Components({
resolvers: [ElementPlusResolver()]
})
]
}
})
# 2.5. axios 集成
安装 axios:
npm install axios |
封装 axios:
import axios, { AxiosInstance, AxiosRequestConfig, AxiosResponse } from 'axios' | |
import { Result } from './types' | |
import { useUserStore } from '/@/store/modules/user' | |
class HYRequest { | |
private instance: AxiosInstance | |
private readonly options: AxiosRequestConfig | |
constructor(options: AxiosRequestConfig) { | |
this.options = options | |
this.instance = axios.create(options) | |
this.instance.interceptors.request.use( | |
(config) => { | |
const token = useUserStore().getToken | |
if (token) { | |
config.headers.Authorization = `Bearer ${token}` | |
} | |
return config | |
}, | |
(err) => { | |
return err | |
} | |
) | |
this.instance.interceptors.response.use( | |
(res) => { | |
// 拦截响应的数据 | |
if (res.data.code === 0) { | |
return res.data.data | |
} | |
return res.data | |
}, | |
(err) => { | |
return err | |
} | |
) | |
} | |
request<T = any>(config: AxiosRequestConfig): Promise<T> { | |
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { | |
this.instance | |
.request<any, AxiosResponse<Result<T>>>(config) | |
.then((res) => { | |
resolve((res as unknown) as Promise<T>) | |
}) | |
.catch((err) => { | |
reject(err) | |
}) | |
}) | |
} | |
get<T = any>(config: AxiosRequestConfig): Promise<T> { | |
return this.request({ ...config, method: 'GET' }) | |
} | |
post<T = any>(config: AxiosRequestConfig): Promise<T> { | |
return this.request({ ...config, method: 'POST' }) | |
} | |
patch<T = any>(config: AxiosRequestConfig): Promise<T> { | |
return this.request({ ...config, method: 'PATCH' }) | |
} | |
delete<T = any>(config: AxiosRequestConfig): Promise<T> { | |
return this.request({ ...config, method: 'DELETE' }) | |
} | |
} | |
export default HYRequest |